A papilloma in the neck is one of the manifestations of an infectious disease caused by the human papilloma virus. Refers to benign skin formation.
What causes papillomas on the neck
There's a root reason why papillomas begin to develop on the neck or in any other area of the human body - infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), a member of the Papovaviridae family. There are more than 100 serotypes of this pathogen, each responsible for the appearance of the disease's different clinical scene (papilloma, papilloma, warts - these concepts are synonymous, different names are related to the peculiarities of the local area in a particular area).
The main ways of transmission are family and sexual contact (tumors around the anus). The virus can only enter the skin when there is a small wound or an open wound, in other cases the virus cannot cross the protective barrier of the skin.
Information about pathogens
- It is highly contagious regardless of gender (however, it manifests itself more often in women than in men), age or region (according to some sources, 2/3this virus infected planet).
- Contains double helix DNA, capable of integration into the human genome.
- Infection with some virus strains has a high risk of causing cancer, especially in case of permanent injury. Cervical papillomas are caused by strains of viruses that do not cause cancer.
- A virus goes through two main stages in its division. In the initial stage, it is in an intermittent (free) form, and during the same period, the main division of the virus particles occurs. This stage is reversible (after treatment, long-term remission occurs). At the second stage - integration - the virus is implanted into the cell genome (the first step leads to cell degeneration and malignant tumor formation). The first stage is transient and passes relatively quickly, while the second stage is latent and explains the existence of carriers.
- The basal layer of the epidermis, where the virus multiplies, is affected. In the remaining layers, the pathogen can survive, but not divide. Provided that the virus is in the seed layer, as it develops, normal cell differentiation in all layers of this area is disrupted, especially at the level of the papillary layer.
- Tend to have asymptomatic long-term transport in the body (from several months to a year). It is very rare to identify a specific time of infection - this is why treatment begins during a period of clinical manifestation rather than at the first vague signs.
- To prevent infection, the divalent and quadrivalent vaccines are used, which are particularly effective against the most carcinogenic strains 16 and 18.
Factors that influence
- Lack of hygiene. Because the virus has the ability to maintain living in the outside environment for a long time, when going to public places (swimming pools, bathrooms, gyms) it is necessary to carefully follow the rules of defense. individual birth.
- The wound caused by an injury to the skin. For the virus to enter, small cracks or abrasions in the skin (for example, by rubbing the neck with the collar of a shirt) are sufficient.
- Impaired immune system function. With an immune deficiency of any genesis, favorable conditions arise for the development of any infectious disease. For example, frequent colds and infectious diseases lead to weakened immune systems and papillomas on the skin.
- Self-infection when skin is scratched.
- Systematic lifestyle disorder (stress, inactivity, inadequate diet). These factors affect the work of all metabolic processes in the body and lead to a decrease in the skin's barrier function.
- Environmental factors affect the reduced body's defenses (hypothermia, overexposure to ultraviolet rays).
Outward manifestations of the disease
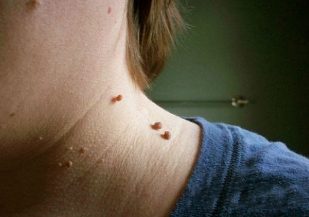
The cervical papilloma in the image looks like this:
- Growth is usually on a broad base that is much higher than the surface of the skin. Less commonly, the base of the papilloma is indicated by a thin leg (in this case, the formation with a hanging position). In the second option, the risk of injury is much higher.
- The boundaries of education are uniform and clear.
- The color does not differ from the surrounding skin. In rare cases, it may be slightly paler or darker than the nearby tissues.
- The surface is usually flat, smooth. It can sometimes develop at the tip of the papilloma, causing the surface of the tumor to be ribbed.
- Diameter varies widely - from 1-3 mm to several centimeters (papillomas of small diameter are more common).
- Position on any area of the neck (back, front). Sometimes the face is involved.
As a rule, there are multiple lesions located along the skin folds.
In very rare cases, the papilloma on the neck can become malignant, that is, degenerate into a skin tumor. This can happen from infection with a cancer-causing strain of HPV.
Signs that may indicate a malignant transformation are as follows:
- color changes and heterogeneity (polymorphism);
- changes the border (blurs, defocuses);
- appearance of asymmetry (when drawing a line through the conditional medium of formation, it is not possible to obtain two equal halves);
- intensive growth;
- bleeding or ulceration (a nonspecific symptom, as it is also typical for simple trauma to cancer);
- itching, burning, or peeling of the skin; The dropout
- is formed (little girl formation around the center).
The appearance of such signs is not necessarily degeneration of papilloma, but it does mean you need to consult a doctor and make a differential diagnosis, find out if we areare talking about a common inflammatory mole or skin cancer.
How to get rid of papillae on the neck
Treatment of papillae on the neck is done only in a complex manner with a simultaneous impact on the pathological focus on the skin and the pathogen itself in the blood.
There are several ways to fight:
Method |
Description |
Medication |
The use of cytostatic, immunomodulatory drugs designed to prevent replication of the viral agent in the affected area and reduce its concentration in the blood. Some drugs (keratolytic agents) are applied directly topically to destroy skin growth (numbness and tissue necrosis). |
Physical methods |
Cryotherapy, laser therapy, coagulation. They aim to remove papillomas on both the neck and other parts of the body. These methods allow you to restore the aesthetics of the exposed skin and remove the reservoir of the virus - a tumor in the skin, but they do not completely remove the virus from the body. |
Combination therapy |
Combines the previous two options and is therefore the most effective. |
Treating papillomas with home folk remedies (eg, cineraria) is ineffective and often dangerous, in any case a prerequisite is to consult a doctor.
Methods of physical destruction
It is possible to effectively reduce the formation by the following physical methods:
Method |
Description |
Local effect with concentrated acid solution |
Use a solution of 1. 5% zinc chloropropionate in 50% 2-chloropropionic acid, a combination of nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic and copper nitrate trihydrate, etc. v. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis by a specialist (dermatologist, cosmetologist) adhering to the surgical rules. . . The agent is applied in the metallic direction with a spatula until the color of the forming substance turns a lighter color (as soon as this has happened, further use should be stopped immediately). To completely treat genital warts, on average you need to perform 1-2 treatments. |
Capacitors |
Using a special electric knife, removal of each forming point is performed without affecting the underlying tissues (with only a minimal impact on healthy skin cells). This method is most convenient when forming a long body and small size. |
Cryodestruction |
The focus of exposure to liquid nitrogen, extremely low temperatures, leads to tissue necrosis. It's good to clean up this kind of education with this broad base. Nitrogen action time selected by experts (1-5 minutes). After heating, a burn is formed, which heals within an average of 10 days. |
Laser removal |
The most modern and most sophisticated method for removing tumors in prominent locations like the neck. There are the most positive reviews. With the help of light guides from 5 seconds to 3 minutes in continuous mode, they work on focus. The cure time is much shorter than with other methods (5-7 days). The technique involves minimal injury to surrounding tissue due to the high precision of the action. |
Classical resection (scalpel excision) |
Used extremely rarely, only with large lesions or suspected malignancy. The reason is that the lesions are often many, scattered around the neck and too small to remove, in addition, after the resection can leave scarring, which creates a cosmetic defect. |














































































